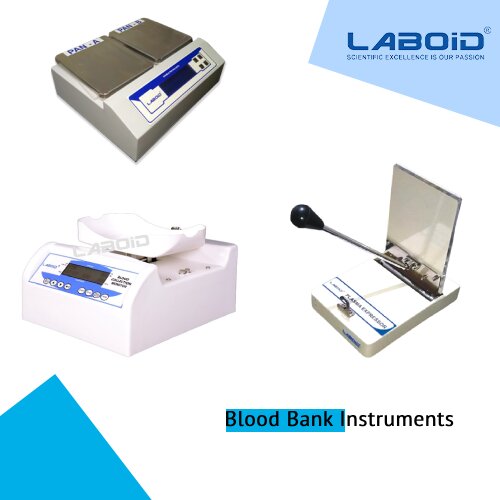
Blood banks play a critical role in the healthcare system by collecting, processing, and storing blood and its components for transfusion purposes. To ensure the safety and efficiency of these processes, blood bank instruments, such as those provided by Laboid International, are utilized. In this article, we will explore the capabilities of Laboid International’s blood bank instruments in handling both whole blood and blood components, highlighting their importance in maintaining the integrity and availability of these life-saving resources.
Whole Blood Handling:
Blood bank instruments are designed to handle whole blood, which consists of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. These instruments facilitate the collection and processing of whole blood, ensuring its preservation and suitability for transfusion. Common blood bank instruments used for whole blood handling include blood collection bags, refrigerated centrifuges, and blood bank refrigerators. These instruments are equipped with features that maintain the appropriate storage conditions, prevent contamination, and facilitate the separation of blood components.
Blood Component Separation:
Blood components, such as red blood cells, platelets, plasma, and cryoprecipitate, have specific therapeutic applications. Blood bank instruments are capable of separating these components through a process known as apheresis or fractionation. Apheresis machines are sophisticated instruments that collect a specific blood component while returning the remaining components to the donor. This allows for the selective collection of blood components, such as platelets or plasma, while preserving the donor’s red blood cells. Fractionators, on the other hand, are used in large-scale blood processing facilities to separate and purify blood components for commercial use.
Automated Blood Processing Systems:
With advancements in technology, blood banks are increasingly adopting automated blood processing systems. These systems streamline the processing of whole blood and blood components, improving efficiency and reducing the risk of errors. Automated systems can perform tasks such as blood component separation, labeling, and inventory management with greater accuracy and speed. They also enhance traceability and documentation, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. Automated blood processing systems are particularly beneficial for large blood banks and transfusion centers that handle a high volume of blood products.
Quality Control and Testing:
Blood bank instruments are not only responsible for handling and processing blood products but also for ensuring their safety and quality. These laboratory equipment manufacturers instruments are equipped with features for quality control and testing, including compatibility testing, blood typing, and screening for infectious diseases. Blood bank instruments, such as automated analyzers and serology testing systems, enable efficient and accurate testing of blood samples, ensuring that only compatible and safe blood and blood components are transfused to patients.
Maintenance and Calibration:
To ensure the reliability and accuracy of blood bank instruments, regular maintenance and calibration are essential. Blood bank instruments undergo routine maintenance procedures, including cleaning, calibration checks, and performance evaluations. These measures help to identify and rectify any issues or deviations, ensuring the instruments are functioning optimally and producing accurate results. Regular maintenance also extends the lifespan of the instruments, reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns and interruptions in blood processing operations.
Blood Component Storage and Preservation:
Blood bank instruments, such as blood bank refrigerators and freezers, are designed to provide optimal storage conditions for different blood components. Red blood cells, for example, require refrigeration at specific temperatures to maintain their viability and function. Platelets, on the other hand, need to be stored at controlled room temperature to prevent cold-induced damage. Blood bank instruments ensure that each blood component is stored under appropriate conditions to preserve their therapeutic properties.
Transfusion Compatibility Testing:
Blood bank instruments play a crucial role in transfusion compatibility testing, which involves determining the compatibility between the donated blood and the intended recipient. Instruments such as automated blood typing systems and cross-matching analyzers facilitate quick and accurate determination of blood types and the presence of antibodies. These instruments help ensure that the transfused blood is compatible with the recipient, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
Conclusion:
Blood bank instruments, such as those provided by Laboid International, play a crucial role in handling both whole blood and blood components. From collection and processing to testing and quality control, Laboid International’s instruments ensure the safety, integrity, and availability of blood products for transfusion. With advancements in technology, automated systems offered by Laboid International have further enhanced the efficiency and accuracy of blood bank operations. By employing reliable and well-maintained blood bank instruments from Laboid International, healthcare facilities can effectively manage the supply and demand of blood and its components, ultimately saving lives and improving